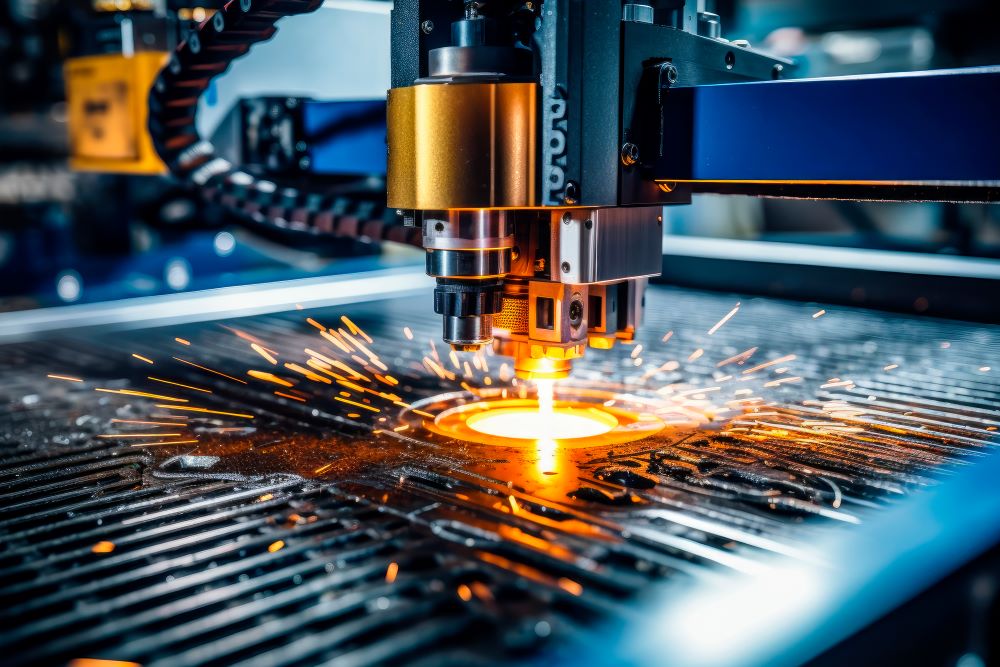
Plasma welding, or plasma arc welding (PAW), is used in many industrial sectors. A versatile and high-performance welding technique, the plasma welding process can be used to produce top-quality welds.
HARtech’s industrial welding professionals take a closer look at plasma welding, explaining how it works, what it’s used for and the benefits it offers. Learn how this innovative welding technique can help your business.
How plasma welding works
Plasma welding is an advanced welding technique that uses a high-temperature, ionized gas known as plasma to create and maintain an electric arc between a welding electrode and a workpiece. The intense heat generated by the plasma arc melts the base metal and filler material (if used) resulting in a strong and precise weld.
In the plasma welding process, an inert gas (e.g. argon) creates a protective environment around the arc and weld zone, which prevents contamination of the weld by oxygen from the air and guarantees a high-quality weld.
Common uses for plasma welding
Plasma welding is widely used in many industrial sectors. Applications include the automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, industrial machinery design and petrochemical industries. Plasma welding is used to build pipes, tanks, metal structures, engine parts, cutting tools and more.
Since it can be used on different types of material, plasma welding is a highly sought-after welding technique. Plasma welding helps improve the productivity, quality and efficiency of various manufacturing and construction processes.
Stages of the plasma welding process
To perform efficient, high-quality plasma arc welding, a complete understanding of the plasma welding process is essential. Read on to learn more.
Preparing parts for welding
Before beginning the plasma welding process, it is essential to prepare all parts. This includes cleaning surfaces to remove contaminants such as rust, grease or paint residues. Chamfering or deburring may also be necessary, to make sure fusion and metal adhesion are successful and you obtain a high-quality weld.
Setting up plasma welding equipment
It’s time to set up the plasma welding equipment. This involves mounting the electrode, connecting the power supply and shielding gas cables, and checking all safety parameters. Plasma welding equipment generally includes a power source, a plasma welding torch and a cooling system.
Plasma welding parameters and settings
There’s one more step before you start welding. Adjust settings and parameters according to the material you are welding, the thickness of the parts and any welding specifications. You will need to verify electric current intensity, wire feed speed, shielding gas pressure, the distance between the electrode and workpiece, and other variables specific to your plasma welding project. A professional welder-assembler can guarantee the precision of settings and parameters for optimum metal fusion and penetration.
Creating the weld
The operator directs the plasma welding torch along the welding area, which generates an electric arc and intense plasma. The thermal energy of the plasma melts the base metals and filler material, forming a solid, homogeneous weld. The operator must use proper welding technique, control feed speed and maintain a constant distance between the torch and workpiece to achieve optimum results.
Industrial plasma welding
Plasma welding is highly adaptable and used in a wide range of industries. Its versatility, precision and reliability make it the preferred choice for many demanding welding applications.
Plasma welding in the metal construction industry
Plasma welding has many applications in the steel construction industry. Thanks to its ability to produce precise, high-quality welds, plasma welding is widely used to join steel structures, beams, frames and other structural elements. Plasma welding produces strong, aesthetically pleasing welds that are resistant to mechanical stress and the elements. It is versatile and cane be used to weld metals of different thicknesses and compositions.
Plasma welding in the automotive industry
Plasma welding is also widely used to manufacture and assemble car parts. It is an effective method for creating precise, high-quality welds on bodies, chassis, exhaust systems and fuel tanks. Plasma welding offers high weld strength and durability, essential for ensuring the safety and longevity of vehicles. It also produces clean, aesthetically pleasing welds, meeting the high aesthetic standards of the automotive industry.
Plasma welding in the aerospace industry
The aerospace industry requires welds of exceptional quality to guarantee the reliability and safety of aircraft and satellites. Plasma welding can produce precise, strong, defect-free welds, and is used to join aircraft structures, fuel tanks, piping and other critical components. Plasma welding produces lightweight, strong welds that meet the stringent performance and safety requirements of this demanding industry.
Plasma welding benefits and limitations
Now that we’ve explored how plasma welding works and the stages involved in the process, let’s look at some of the benefits and limitations of this welding technique.
The benefits of plasma welding
Plasma welding can be used to produce high quality welds. Thanks to the intense concentration of heat generated by the plasma arc, plasma welds are generally free from defects such as porosity, cracks or inclusions. The process creates total fusion of materials, ensuring a solid, homogeneous connection.
What’s more, plasma welds are precise. The plasma arc can be rigorously controlled, resulting in narrow, deep welds – ideal for items requiring high precision, such as small parts or thin materials. Precise welds also reduce the amount of material to be removed during finishing, which simplifies post-processing operations.
The limits of plasma welding
Despite its many advantages, plasma welding also has certain limitations. It requires specialized equipment, including a plasma arc generator and plasma welding torches. Installation and maintenance costs can be higher than for other types of welding.
Plasma welding also generates very high temperatures, which can cause welded parts to deform. During plasma welding requires, extra effort is required to minimize distortion, such as using special cooling devices.
Finally, plasma welding may not be a good choice for applications that demand high mobility or involve restricted access. The size of the equipment and the demands of handling the plasma arc make it more difficult to weld in tight spaces or hard-to-reach positions. In these cases, you’re better off using TIG welding or MIG-MAG welding.
HARtech’s plasma welding services
If you need to create high-quality welds, work on precise joints or be able to weld a variety of materials, plasma welding could be the right solution.
You can count on HARtech’s knowledge and experience for your company’s industrial welding needs. We have extensive expertise in plasma welding and other types of welding. As industrial welding professionals, we offer a qualified team equipped with the latest welding technologies.
Whether you have construction, repair or manufacturing projects requiring superior quality welds, HARtech is ready to meet your specific challenges and needs. Contact us now to take advantage of our services.